# Best Security Practices
# Software Updates
To ensure the security of your system, follow these best practices:
- Use HTTPS to encrypt communication. Google now considers HTTPS as a ranking factor.
- Keep all software on the server up-to-date, including Krayin, the database, Adminer/phpMyAdmin, Apache, Redis, etc.
- Regularly update the server operating system to apply available security patches.
- Manage files only through secure communication protocols like SSH, SFTP, or HTTPS. Disable FTP.
- Use the
.htaccessfile to protect system files when using the Apache web server. - Disable unused ports and stop unnecessary services running on the server.
- Restrict access to the admin panel by allowing only specific IP addresses and enforcing two-factor authorization for admin logins.
- Ensure the use of strong and unique passwords.
- Configure and update the firewall properly to secure the connection between payment card data and the public network.
# Limiting Error Messages
To limit the exposure of sensitive information in error messages, follow these steps:
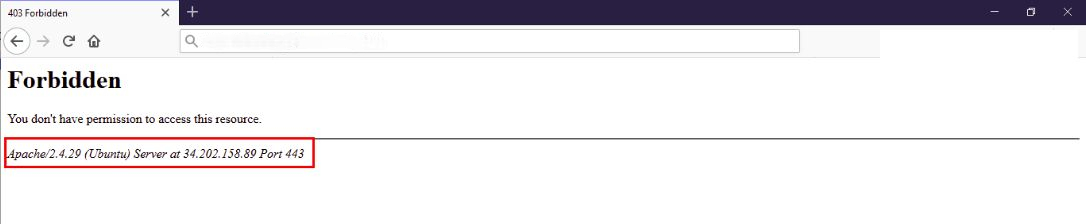
- Edit your Apache configuration file to avoid displaying server and operating system details.
- Set
ServerSignaturetoOff(by default, it isOn). - Add
ServerTokens Prodto display Apache only as the product.
Screenshot
# Limiting Admin Access
To restrict access to the admin area, modify the .htaccess file with the following code:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} .*/admin
RewriteCond %{REMOTE_ADDR} !=<IP address>
RewriteCond %{REMOTE_ADDR} !=<IP address>
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ - [R=403,L]
Ensure that there are no accessible development leftovers on the server, such as "log files," ".git directories," "database dumps," or "zip files."
# Restricting Unnecessary Files
To restrict access to unnecessary files, add the following code to your .htaccess file:
<FilesMatch "\.(git|zip|tar|sql)$">
Require all denied
</FilesMatch>
Consider using a Web Application Firewall (WAF) to analyze traffic and detect suspicious patterns, such as credit card information being sent to attackers. Additionally, restrict public access to only ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS), while blocking other ports.
# Restricting PHP Execution Inside Storage
To restrict PHP execution inside the storage directory, modify your Apache configuration file:
<Directory "~/www/krayin/public/storage/">
<FilesMatch "\.php$">
Require all denied
</FilesMatch>
php_flag engine off
</Directory>
Don't forget to restart Apache after making these changes.
# Server Hardening
Take the following measures to harden your server:
- Use the
mod_securitymodule to detect and prevent intrusions. - Implement the
mod_passivemodule to prevent brute force attacks. - Allow only specific users to log in.
- Disable login for users with empty passwords.
- Review and configure iptable rules to prevent unauthorized access and activity.
- Regularly back up important files and store them remotely in a secure environment.
# Strong Passwords
Ensure the use of strong and unique passwords and encourage periodic password changes. You can use a password generator tool (Password Generator (opens new window)) to create strong passwords. Limit access to the Krayin admin
panel by updating the whitelist with authorized IP addresses.
# Implementation of HTTP Security Headers
Implementing the following HTTP security headers enhances web security:
# HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)
Set the Strict-Transport-Security response header to instruct the browser to only access the application using HTTPS:
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=<expire-time>
# Cross-Site Scripting Protection (X-XSS Protection)
Set the X-XSS-Protection response header to enable browsers to detect and prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks:
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
# X-Frame-Options
The X-Frame-Options response header protects applications against clickjacking. It specifies whether the content can be displayed within frames:
X-Frame-Options: deny
# X-Content-Type-Options
The X-Content-Type-Options response header forces the browser to disable MIME sniffing, preventing MIME sniffing vulnerabilities:
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
# Content Security Policy (CSP)
Implement a Content Security Policy (CSP) response header to control resources that can be loaded in users' browsers. CSP helps detect and mitigate attacks such as XSS and clickjacking.
# Continuous Logging And Monitoring
Maintain continuous logging and monitoring of all network access and cardholder data activities. Keep an eye out for large volume orders of a single item from new customers, a series of orders shipped to the same address but using different payment methods.
By implementing these best security practices, you can enhance the security of your system and protect it from potential threats.